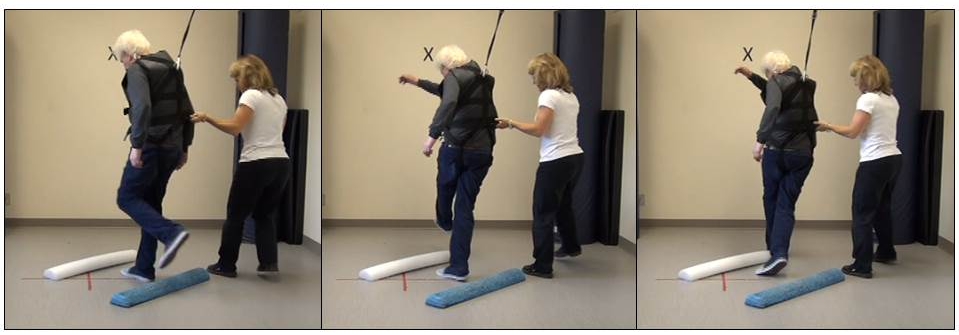
Reactive balance training
Summary
Many people, like older adults and people with neurological illness or injury, are increased risk for falls. There is good evidence that physical exercise can prevent falls by improving balance. We want to know if we can make fall prevent exercises even more effective. In order to keep from falling down, people must often perform rapid and sophisticated balance reactions. Our research explores novel training techniques in order to retrain these rapid reactions. The findings from this research work will provide essential information about the optimal ways to train rapid balance reactions. We expect that this training has the potential to not only prevent falls, but to also improve safe independent mobility and engagement in daily activities.
This research contributed to our reactive balance toolkit, aimed at helping therapists to use reactive balance training in their settings. Please visit https://kite-uhn.com/tools/rebal for more information.
Funding
Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, Undergraduate Student Research Award, Sarah Thompson (2023)
Heart and Stroke Foundation Canadian Partnership for Stroke Recovery, Collaborative Catalyst Grants: Dose and Timing (2019-2022)
Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Grant-in-Aid (2018-2021)
Heart and Stroke Foundation Canadian Partnership for Stroke Recovery, Collaborative Innovation Grant (2018-2020)
Ministry of Research and Innovation, Early Researcher Award (2015-2020)
Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Open Operating Grant (2014-2017)
Heart and Stroke Foundation Canadian Partnership for Stroke Recovery, Catalyst Grant (2015-2016)
Trainees
Augustine Joshua Devasahayam (post-doctoral fellow)
Azadeh Barzideh (PhD student)
Sarah Thompson (former undergraduate student)
Tyler Saumur (former PhD student)
Andrew Huntley (former post-doctoral fellow)
Janelle Unger (former PhD student)
Gabriela Rozanski (former post-doctoral fellow)
Chris McCrum (former visiting scholar)
Alison Schinkel-Ivy (former post-doctoral fellow)
I am currently recruiting new trainees to work on this project
Papers
Margalit N, Kurz I, Wacht O, Mansfield A, Melzer I. A survey of Israeli physical therapists regarding perturbation-based balance training. BMC Geriatrics. 2023;23:656. doi:10.1186/s12877-023-04356-5
Jagroop D, Aryan R, Schinkel-Ivy A, Mansfield A. Reliability of unconventional centre of pressure measures of quiet standing balance in people with chronic stroke. Gait and Posture.2023;102:159-163. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2023.03.021
Devasahayam AJ, Farwell, K, Lim B, Morton A, Fleming N, Jagroop D, Aryan R, Saumur TM, Mansfield A. The effect of reactive balance training on falls in daily life: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys Ther. 2023;103(1):pzac154. doi:10.1093/ptj/pzac154
Unger J, Singh H, Mansfield A, Masani K, Musselman K. The experiences and impact of intensive balance training for people with incomplete spinal cord injury or disease: a qualitative study. Spinal Cord. 2022;60:1062-1068. doi:10.1038/s41393-022-00823-9
Mansfield A, Danells CJ, Inness EL, Musselman K, Salbach NM. A survey of Canadian healthcare professionals’ practices regarding perturbation-based balance training. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice. 2021;7(37):787-800. doi:10.1080/09593985.2019.1650856
Unger J, Chan K, Lee JW, Craven BC, Mansfield A, Alvaninia M, Masani K, Musselman K. The effect of perturbation-based balance training and conventional intensive balance training on reactive stepping ability in individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury or disease: a randomized clinical trial. Frontiers in Neurology. 2021;12:620367. doi:10.3389/fneur.2021.620367
Mansfield A, Inness EL, Danells CJ, Jagroop D, Bhatt T, Huntley AH. Determining the optimal dose of reactive balance training after stroke – study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e038073. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038073
Barzideh A, Marzolini S, Danells CJ, Jagroop D, Huntley A, Inness EL, Mathur S, Mochizuki G, Oh P, Mansfield A. The effect of reactive balance training on physical fitness post-stroke: study protocol for a randomized non-inferiority trial. BMJ Open. 2020;10;e035740. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035740
Schinkel-Ivy A, Huntley AH, Danells CJ, Inness EL, Mansfield A. Improvements in balance reaction impairments following reactive balance training in individuals with sub-acute stroke: a prospective cohort study with historical control. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation. 2020;27(4): 262-271. doi:10.1080/10749357.2019.1690795
Unger J, Chan K, Scovil CY, Craven BC, Mansfield A, Masani K, Musselman KE. Intensive balance training for adults with incomplete spinal cord injuries: protocol for an assessor-blinded randomized clinical trial. Physical Therapy. 2019;99(4):420-427. doi:10.1093/ptj/pzy153
Schinkel-Ivy A, Huntley AH, Aqui A, Mansfield A. Does perturbation-based balance training improve control of reactive stepping in individuals with chronic stroke? Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2019;28(4):935-943. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.12.011
Mansfield A, Aqui A, Danells CJ, Knorr S, Centen A, DePaul VG, Schinkel-Ivy A, Brooks D, Inness EL, Mochizuki G. Does perturbation-based balance training prevent falls among individuals with chronic stroke? A randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e021510 doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021510
Mansfield A, Schinkel-Ivy A, Danells CJ, Aqui A, Aryan R, Biasin L, DePaul VG, Inness EL. Does perturbation training prevent falls after discharge from stroke rehabilitation? A prospective cohort study with historical control. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26(10):293-304. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.04.041
Gerards M, McCrum C, Mansfield A, Meijer K. Perturbation-based balance training for falls reduction among older adults: current evidence and implications for clinical practice. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17(12):2294-2303. doi:10.1111/ggi.13082
Mansfield A, Wong JS, Bryce J, Knorr S, Patterson KK. Does perturbation-based balance training prevent falls? A review and meta-analysis of preliminary randomized controlled trials. Phys Ther. 2015;95(5):700-709. doi:10.2522/ptj.20140090
Mansfield A, Aqui A, Centen A, Danells CJ, DePaul VG, Knorr S, Schinkel-Ivy A, Brooks D, Inness EL, McIlroy WE, Mochizuki G. Perturbation training to promote safe independent mobility post-stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Neurol. 2015;15:87. doi:10.1186/s12883-015-0347-8
Mansfield A, Inness EL, Komar J, Brunton K, Biasin L, Lakhani B, McIlroy WE. Training rapid stepping responses in an individual with stroke: a case report. Phys Ther. 2011;91(6):958-969. doi:10.2522/ptj.20100212
Mansfield A, Peters AL, Liu BA, Maki BE. Effect of a perturbation-based balance training program on compensatory stepping and grasping reactions in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Phys Ther. 2010;90(4):476-491. doi:10.2522/ptj.20090070
Mansfield A, Peters AL, Liu BA, Maki BE. A perturbation-based balance training program for older adults: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2007;7:12. doi:10.1186/1471-2318-7-12